What is the role of the cathode current collector in a battery?
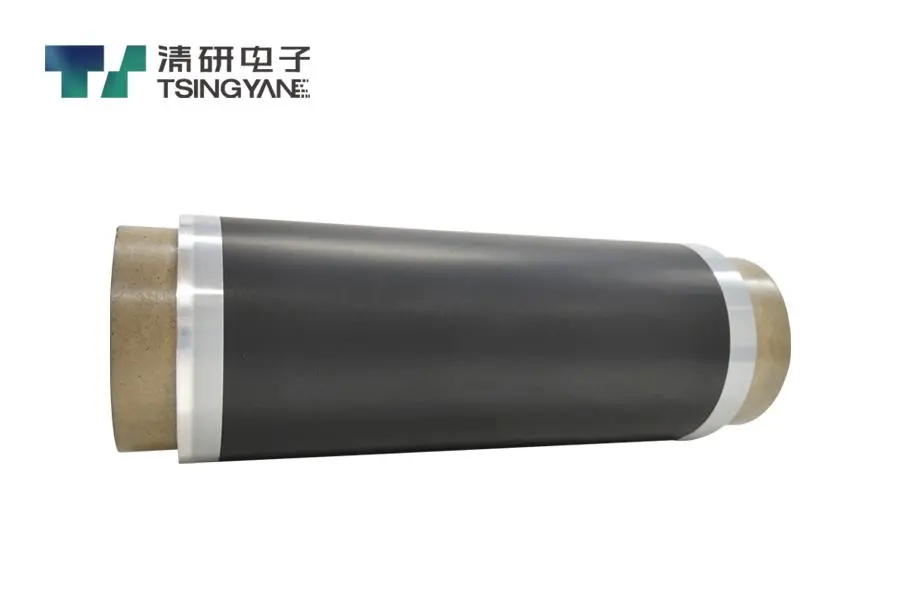
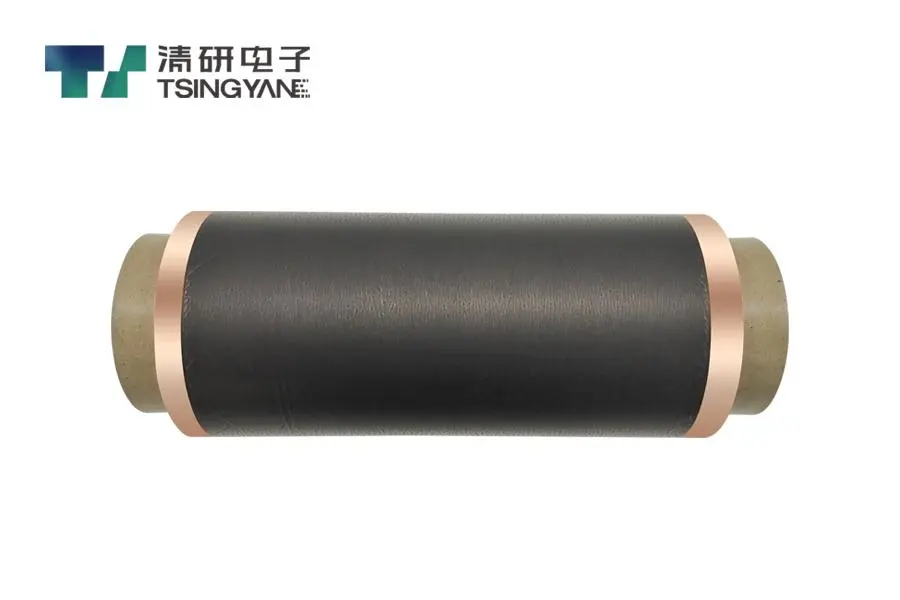
The cathode current collector, typically made of aluminum current collector material like aluminum foil, is used in a lithium ion battery due to its excellent electrical conductivity and stable electrochemical performance at high voltages.
What is the function of a current collector in battery?
The primary role of a current collector in battery systems is to facilitate the transfer of electrons between the active material and the battery’s external terminals, such as a busbar collector in some setups.
How do anode current collector and cathode current collector currents differ?
The anode current collector is where current flows into the electrode, while the cathode current collector is where current flows out. Typically, the anode current collector is the positive side, and the cathode current collector is the negative side in a lithium ion battery.
What distinguishes a battery current collector from an electrode?
A battery current collector, such as a metal foil often coated with a carbon current collector layer like graphene, forms the base, while an electrode in a lithium ion battery includes the battery current collector plus an active material layer applied to its surface.
What are the various types of current collectors for sale?
Current collectors for sale include several designs: a) perforated (circular) collectors, b) parallel channel collectors, c) non-rectangular parallel channel collectors, and d) metal mesh current collectors available from a current collector supplier.
Why is a copper current collector used for anode current collectors?
A copper current collector is commonly chosen as the anode current collector in a lithium ion battery due to its high conductivity, good flexibility, chemical stability, affordability, and lack of reaction with lithium at room temperature, making it ideal for studying lithium deposition, as supported by research from a current collector manufacturer.
Which is more powerful, the anode or the cathode in a current collector lithium ion battery?
The positive electrode has a higher potential than the negative electrode in a current collector lithium ion battery. During discharge, the positive electrode acts as the cathode current collector, and the negative electrode is the anode current collector. During charging, the positive electrode becomes the anode current collector, and the negative electrode becomes the cathode current collector.
What is the purpose of a current collector for overhead system in batteries?
The primary purpose of a current collector for overhead system or a battery current collector is to enable electron flow between the active material and the battery’s external terminals, ensuring efficient operation in systems like those supplied by a current collector supplier.

 English
English 日本語
日本語 한국어
한국어 français
français Deutsch
Deutsch Español
Español italiano
italiano русский
русский português
português العربية
العربية tiếng việt
tiếng việt